Report Materials
KEY RESULTS
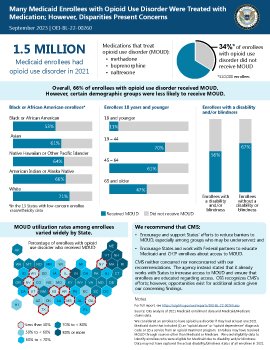
One-third of the 1.5 million Medicaid enrollees with opioid use disorder did not receive medication treatment (referred to as MOUD) in 2021. Certain demographic groups—including Black or African American enrollees; enrollees 18 years of age and younger; and enrollees with a disability and/or blindness—were less likely to receive MOUD. In 10 States, less than half of enrollees with opioid use disorder received MOUD.
WHY WE DID THIS STUDY
Nearly 81,000 people died from opioid overdoses in the United States in 2021, an increase of 17 percent from the previous year. Treating opioid use disorder with MOUD is essential to reducing overdose deaths; however, many individuals in need experience difficulties accessing this potentially life-saving treatment. For example, the Office of Inspector General found that fewer than one in five Medicare enrollees with opioid use disorder received MOUD in 2021. Individuals seeking treatment often face barriers such as difficulty finding providers who are authorized and/or willing to prescribe or dispense MOUD and stigma surrounding its use. For example, until recently, only providers with a Federal waiver could prescribe or administer buprenorphine for opioid use disorder in an office setting. Research also suggests that particular demographic groups, such as adolescents or people of certain races, may be less likely to receive MOUD. Medicaid covers an estimated 40 percent of nonelderly adults with opioid use disorder, underscoring the program's key role in providing access to MOUD. In this data brief, we examine the extent to which Medicaid enrollees with opioid use disorder received MOUD in 2021.
HOW WE DID THIS STUDY
We used Medicaid claims data to determine the extent to which Medicaid enrollees with opioid use disorder received MOUD through Medicaid in 2021. Because Medicaid enrollees may be dually enrolled in Medicare, we also reviewed Medicare claims data to determine if enrollees who were enrolled in both programs received MOUD through Medicare. Additionally, we used Medicaid enrollment and eligibility data to examine how MOUD treatment rates differed among demographic groups.
WHAT WE RECOMMEND
Our findings underscore the need for continued efforts to increase the use of MOUD in Medicaid. Accordingly, we recommend that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) (1) encourage and support States' efforts to reduce barriers to MOUD, especially among groups who may be underserved; and (2) encourage States and work with Federal partners to educate Medicaid and CHIP enrollees about access to MOUD. CMS neither concurred nor nonconcurred with our recommendations. The agency instead stated that it already works with States to increase access to MOUD and ensure that enrollees are educated regarding access.
View in Recommendation Tracker
Notice
This report may be subject to section 5274 of the National Defense Authorization Act Fiscal Year 2023, 117 Pub. L. 263.